Transistor
- Transistors have two basic functions in computer science:conducts electricity or blocks the flow of electricity, depending on the voltage level of an input signal.
- Transistors are made of semiconductor material (like silicon).
- Semiconductor materials such as silicon that is neither a good conductor(copper) nor a good insulator(rubber)
- Transistors act like a switch although they do not have moving parts.
- 3 Terminals:
- Source: produce electricity for light, etc.
- Base: a gate between the source and ground. Only if the based is charged, source and ground are connected.
- Emitter, typically connected to a ground wire
- When base is charged, the electrical signal is grounded, and it flow through an alternative route to the ground.
- When base is uncharged, the electrical signal flows through an alternative route to the ground.
A Transistor (Dale and John)
NOT Gate Constructed by Transistor: Inverted
(Dale and John)
- When source and Vin are charged(Vin is 1), electrical signal is grounded, Vout is 0.
NAND Gate Constructed by Transistor:
(Dale and John)
- When source, V1, V2 are charged(V1 and V2 are 1); electrical signal is grounded, and Vout is 0.
NOR Gate Constructed by Transistor
(Dale and John)
Circuit
- Combinational circuit
- Boolean expression (AB+AC)
(Dale and John)
- Sequential circuit
- Boolean expression A(B + C)
(Dale and John)
Circuit equivalence
- The same output for each corresponding input–value combination for two circuits
Properties of Boolean algebra
(Dale and John)
Adder
- Adder is a electronic circuit that performs an addition operation on binary values
- Half adder: A circuit that computes a sum of two bits by using XOR Gate (A⊕B) and a carry bit by using AND Gate (AB). For example, if the inputs are 1 and 0, the sum will be 1 and the carry bit will be 0. If the inputs are 1 and 1, the sum will be 0 (since binary system base 2), and the carry bit will be 1.
(Dale and John)
- Full adder A circuit that computes a sum of two bits, an input carry bit (carry-in bit) into account, and two carry-out bits.
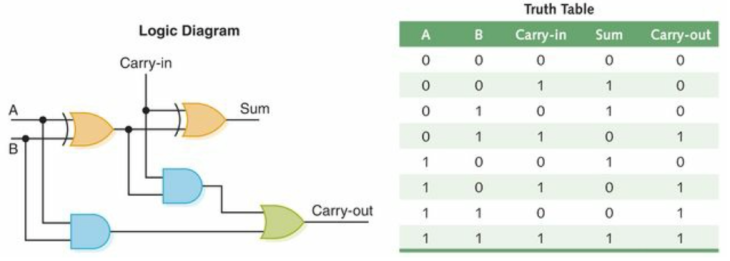 (Dale and John)
(Dale and John)Circuit as Memory
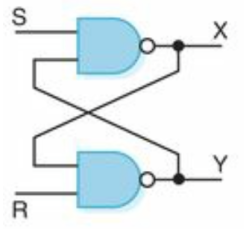 (Dale and John)
(Dale and John)
- sequential circuit
- Two complementary outputs X and Y (0 or 1)
- Value of X: current state of the circuit. (If X is 1, the circuit is storing a 1; if X is 0, the circuit is storing a 0.)
- External input (S or R) and one input coming from the output of the other gate.
Work Cited
Dale, Nell and John Lewis. Computer Science Illuminated. Print.


