Wireless Network has two components: hardware and software.
Hardware Components
There are several example of hayward components of the network: nodes which are the devices on a network (such as laptop, phone, printer); modem which translate electric signals to digital signals for computer; hardware firewall, WAP (Wireless Router / Access Point); switch and hub; wireless Network Adapter / NIC; wireless antennas; wireless repeater which is used as a expander of Wi-Fi signals; and ethernet cable.
Modem translates electric signals to digital signals that computers can understand. The modem and the router looks similar while they actually have different functions. The router shares your network with your multiple devices. The modem is a device that provide access to your internet. So the process is that your device connect to the router, then to the modem, and eventually to the internet. (Malmlund)
Software Components
There are several example of software component: DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) which automatically decide the IP address; firewall Software which controls the data flow; SSID (Service Set Identification) which to differentiate different WLAN; OS (Operating System); WAP (Wireless Application Protocol); and Web Browser.
If you are scrupulous enough, you may discover that there are software firewall and hardware firewall. So what are the similarities and difference between these two? Both of them serve for controlling the data flow but the hardware firewall can protect more devices and more expensive.
Types of Wireless Networks
There are four types of wireless network: WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network), WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network), WMAN (Wireless Metropolitan Area Network), and WWAN(Wireless Wide Area Network). The following table is the comparison of the characteristics of each type.
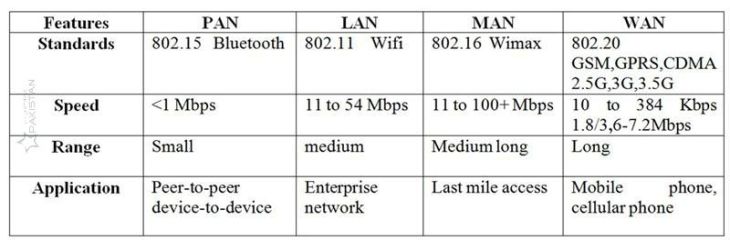
(Types Of Wireless Home)
The following picture shows the examples of each type of wireless network.
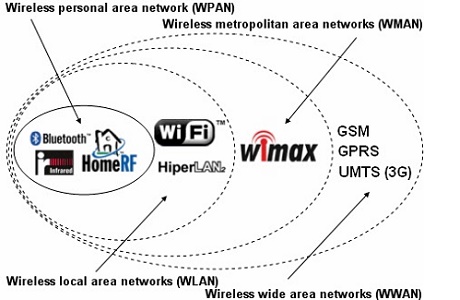
(Wireless Network – Programming)
Wireless Networking Standards 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G
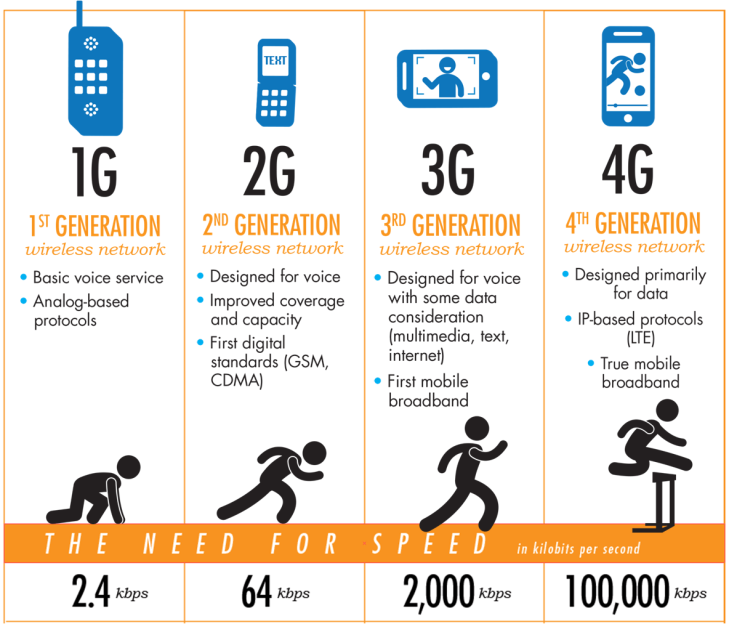 (Cellular Wireless 1G)
(Cellular Wireless 1G)
1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G refer to the five generation of wireless network. 1G only allow voice call and uses analog radio signals. 2G enables calling and texting and uses digital radio signals. 3G enables mobile internet with greater security. 4G offers extremely fast mobile internet. 4G has fixed speed while staying and moving. 4G has faster network reaction time and more stable connection. Theoretically speaking, downloading speed of 4G network is 86 Mbps and the uploading speed id 28.8 Mbps Upload. However, the actual speed is not that fast. It depends of several internal and external factors:
- Distance to the Antenna
- Type of device and Application
- Numbers of users in the area
- Inside or outside
- Available network resources
When a 4G user is sharing files with another 4G users, they can share bandwidth to increasing the transferring speed. Also, 4G uses All-IP technology which means that there is only one single standard communication protocol that is used during transmission.
5G enable massive things to connect with each other. 5G users can connect their phone to their homes, cars, industries, and even the washing machines at home.
4G, LTE, and Wimax
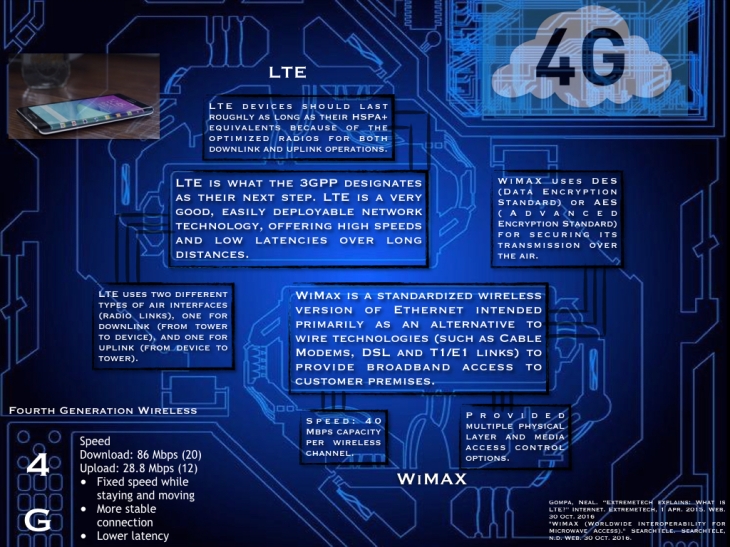
(The poster is made by Michael, Angel, Charles, and Iris)
