Types of Data Loss
Storage devices can be divided broadly into three types: primary, secondary, and tertiary memory.
 (“DBMS Storage System”)
(“DBMS Storage System”)
Primary storage devices can directly access to CPU. Registers, cache memory, and RAM are all examples of primary memory. We can see that most of the primary memory devices are placed inside CPU. All of primary memories are volatile, which means they need continuous power support, otherwise, data will be lost. Primary storage devices are very fast, and the cache memory is the fastest. That’s why primary storage are most frequently accessed by CPU.
Secondary storage devices stored data that will be used in the future or store as backup copies. These devices are outside CPU and non-volatile. Magnetic disks, hard disks, optical disks (CD, DVD) , flash drives, and magnetic tapes are secondary memory devices.
Tertiary storage devices are used to store large volumes of data. They are mostly used to back up a entire system. Tertiary memory has the largest capacity compared to the fastest cache memory but tertiary also has the slowest speed. They are external to the computers. Optical disks and magnetic tapes are tertiary storage devices as well.(Cao, Li and Yang)
Magnetic disk
Magnetic disk is a commonly used secondary storage device. Hard disk are made of metal disk and magnetizable material as cover. A spindle will hang vertically above a hard disk and grave numerous concentric circles on it. Those circles are tracks. Computers can recognize then as 0 or 1.
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)
RAID, a technology, connects multiple secondary devices together. By arranging those secondary storage devices in different ways, they can work together to achieve different goals.
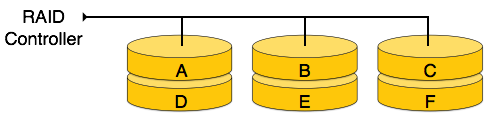
RAID 0
Data will be broke down into different package and store separately in disks. RAID 0 increases the speed of storing while also increase the risk of data loss. It is the tradeoff between speed and security.
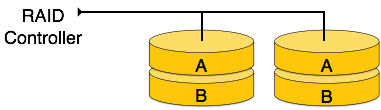
RAID 1
RAID 1 is also called mirror technique. When data is sent to controller, controller send a copy for data to each disk. This process reduces the risk of data loss but it is slower than RAID 0.
Risks of Data Loss
Data Loss occurs when people permanently unable to retrieve files from their date storage.
("What Are The Risks To Data?")
There are many ways that may caused data loss(right side of the following poster). Data loss is risky to individuals, companies, and the nation as a whole.
(Xu, Huang and Zhang)
Prevention of Data Loss
We can store files on cloud storage platform or in external drives like flash drives and hard drives. When you are working on your computer, you should save your work timely. I would like to suggest that you should download a proper virus-killing software and exam the security of your electric devices frequently.
Some people do not know how to use flash drive and had drive appropriately. We need to eject a flash drive out of a computer system before actually pulling it out. We cannot throw an hard drive, otherwise, data inside will be lost. It does not matter to flash drives. However, be nice to your flash drives too.😂😂😂 (Liu, Liu and Song)
Works Cited
“DBMS Storage System”. http://www.tutorialspoint.com. N.p., 2016. Web. 14 Oct. 2016.
Xu, Iris, Angel Huang, and Michael Zhang. “Risks Of Data Loss”. 2016. Presentation.
“What Are The Risks To Data?”. Information Systems & Technology. N.p., 2016. Web. 8 Oct. 2016.
Cao, Charles, Barry Li, and Joe Yang. “Types Of Data Storage”. 2016. Presentation.
Liu, Steven, Bob Liu, and Terry Song. “Prevention Of Data Loss”. 2016. Presentation.